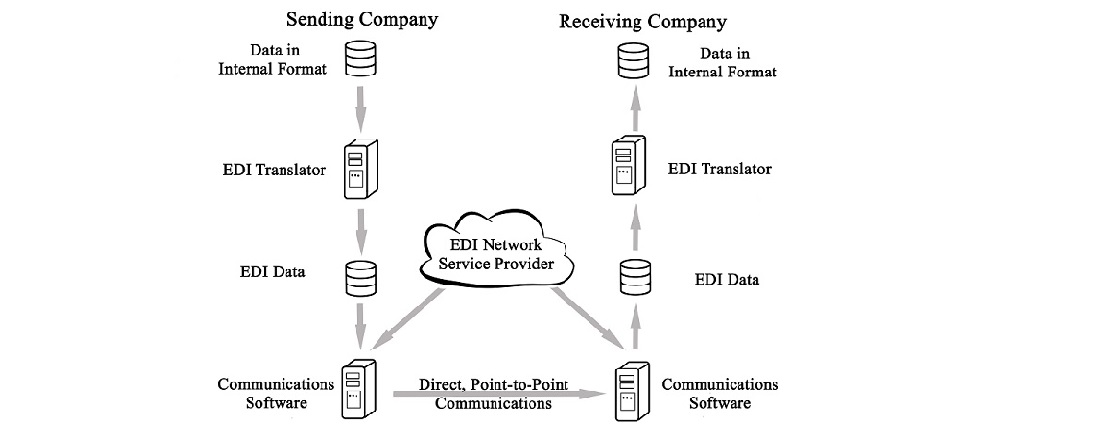
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) refers to the standardized methods of transferring organizational electronic business documents from, and to, different computers for EDI communications. Everything from trading partners to various industries are able to send, receive, and transmit data accurately and securely with the help of these protocols. Below are some of the well-known EDI communication protocols:
API (Application Programming Interface)
An application programming interface is, simply put, a series of rules and protocols to allow for real-time interaction among different software applications. It specifies the methods and formats that a developer might invoke to request and exchange information from one software system to another. APIs and EDI perform the same functions, which is to grant the ability for two business systems to find each other and share data. Such interfaces are necessary to connect vendors to the retailers with whom they do business and also to integrate with other various other systems. But between API or EDI integration choice lies depend upon the fact if the systems involved offer the support for APIs. If they do, then an API shall first be used to initiate a new EDI integration, making it a lot smoother and more efficient.
The API establishes a communication path that allows the establishment of EDI connections but with a wider range of capabilities and greater flexibility. The use of an API in EDI integration offers companies the ability to transcend the limitations inherent in traditional EDI
AS2 (Applicability Statement 2)
AS2, or "Applicability Statement 2," is a protocol that is widely used for secure and reliable transmission of data over the Internet. AS2 is routinely used by companies that use Electronic Data Interchange transactions, such as exchanging sensitive data like purchase orders and invoices. AS2 EDI uses MDNs to indicate, in almost real-time, when messages have been received and their processing status. This gives trading partners better visibility to the delivery process. AS2 is one of the EDIINT (Electronic Data Interchange-Internet Integration) standards and defines how EDI data can be transmitted over the Internet using Internet-based protocols. AS2 is the most frequently used and accepted of the EDIINT standards for EDI transactions and exchanges.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol for transferring files from one computer to another over a TCP/IP-based network, such as the internet. FTP is most commonly used for sharing and managing files, and it is utilized with many modern and older operating systems and applications. FTP is a client-server process. One computer (the client) makes a connection to another computer (the server) to request the file transfer. The client sends commands to the server and the server responds.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol)
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an important protocol used as a format for communication between client (in most cases, web browsers) and a web server on the World Wide Web. HTTP specifies the transfer of data from a web browser to a web server which serves up web pages or other resources moving around the Internet. HTTP describes how resources such as web pages will be requested and transferred. The transfer of HTTP data is modeled on a request-response method. Clients communicate with servers by submitting an HTTP request that consists of an HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) and an HTTP URL (Uniform Resource Locator), which tells the server which resource is to be retrieved or acted upon. The server accepts the request and returns an HTTP response that contains some status information along with, optionally, the content that you requested.
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure)
HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the standard HTTP that allows secure engagement over a computer network, most commonly, the internet. HTTPS adds a layer of protection above HTTP by encrypting the data transferred between a user's web browser and a website's server. HTTPS ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the data being shared over the internet.
SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol)
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) is a network protocol that is primarily used for the safe file transfer of files between a client and server using a reliable data stream. SFTP is created with the intention of providing a higher level of security and therefore, it is used by organizations that require continuous and secure data transfer. Typically, SFTP runs over an SSH (Secure Shell) protocol to provide a secure communication channel for file transfers. In addition, SSH provides stronger encryption and public-key authentication features. SFTP is an open standard that is widely used and supported by many applications and server platforms for secure file transfer.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is an EDI Communication Method used to transmit EDI files over the internet via email.
VAN (Value Added Network)
A Value Added Network (VAN) is a third-party service provider that offers enhanced features and services to facilitate EDI and other data communication between businesses. VANs play a crucial role in enabling secure and efficient communication between trading partners, helping businesses exchange electronic documents, such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices.
How to Choose the Right EDI Communication Method?
The communication method for your EDI file could have a profound impact on the ease and security of data transaction between you and your trading partners. There are several things to consider when deciding the communication method that will be used:
- Trading Partner Requirements: First, you will want to understand the trading partner's EDI requirements. You and different trading partners could be tied to communication method, or they may provide you preference as to the communication methods they support (i.e. AS2, SFTP, FTPS, VAN, etc.). You will want to ensure your choice fits with what the trading partner can accommodate.
- Security Level: Security is always one of the most important considerations when communicating sensitive business data. Review the security protocols available for each communication method. AS2, SFTP and FTPS all offer authentication and encryption for transmitting EDI files, so that you can transmit EDI files in a secure manner. Ensure your choice aligns with your data security requirements.
- Ease of Implementation: While inserting the method into your existing infrastructure, consider how easily this may be accomplished: some may require more extensive setup and configuration than others, which might integrate well with your systems. Evaluate your technical abilities with the resources you have to put this method into practice.
- Compliance and Standards: Verify that the chosen method complies with EDI standards applicable to your industry. Different industries may have their own standard to be adhered to (for example, ANSI X12, EDIFACT). Make sure communication conforms suitably to these standards in either communication.
- Implementation Cost: Consider implementation costs for each method of communication. There are some methods subjecting implementation fees down the line and others charging monthly subscriptions or per-use fees. Compare these against your existing budget and the apparent expected return on investment of EDI integration.
- Redundancy and Reliability: Look for any failover that guarantees the operations are continuous in case there is any server or network failure. Reliability is an essential feature to be considered as it prevents any unrecognized disruption in your EDI processes.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Check on integration capabilities with your existing business systems, for example, your Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, by means of a method chosen. Integration setting would help to smoothen the data from end to end with less manual intervention.
Ultimately, the right EDI file communication method will depend on your specific business needs, trading partner requirements, and technical capabilities. Careful evaluation of these factors will help you make an informed decision that supports your EDI integration goals.
To know more on how we implement EDI and integrate into any of their internal systems, contact our sales department at +1 888-339-0722 or email us at sales@infoconn.com